Synapse Electricity Snapshot 2023
March 9, 2023
Tags:
The 2023 Synapse Electricity Snapshot highlights several major trends in 2022 electric sector capacity, generation, CO2 emissions, and related statistics. Our key findings include the following:
- For the first time, renewable capacity (inclusive of wind, solar, and battery storage resources) exceeds capacity from coal. As of the end of 2022, there were over 225 GW of renewable capacity installed, compared to coal’s 216 GW. Together, non-CO2-emitting generating capacity makes up 34 percent of the nationwide total and accounts for 38 percent of all generation.
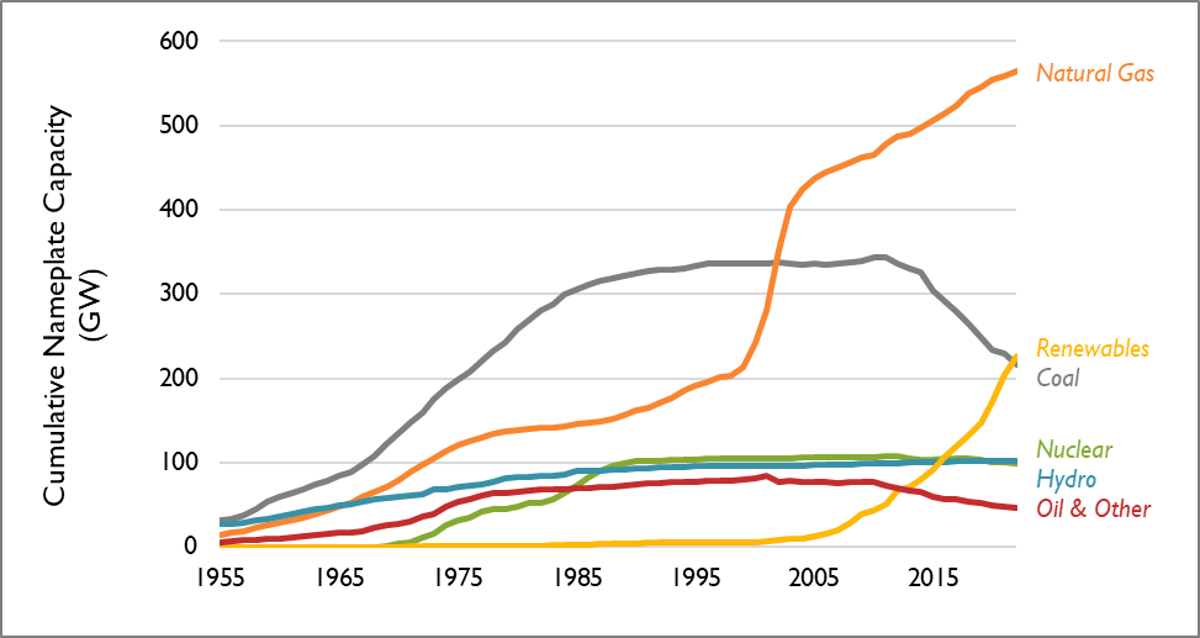
Note: This figure displays net nameplate values for utility-scale generators; annual capacity retirements are subtracted from annual capacity additions.
- Retirement of old and uneconomic coal plants, coupled with the low marginal costs of other resources like gas, wind, and solar, has led to the lowest level of coal generation since the early 1970s.
- From 2021 to 2022, annual electricity sales increased by 3 percent, the highest year-on-year growth observed since the United States transitioned out of a recession in 2009 to 2010.
- Since reaching an all-time peak in 2007, electric sector CO2 emissions have declined to 1,534 million metric tons in 2022, second behind in 2020 in terms of having the lowest level of emissions since the 1970s.
- Since 1990, CO2 emitted per dollar of GDP has decreased by 60 percent, from 0.15 to 0.06 kg per dollar.
For more insight into the latest electric-sector data, read the 2023 Synapse Electricity Snapshot.