Synapse Handbook Provides Guidance for Designing, Implementing Utility Performance Incentive Mechanisms
Long used to encourage utilities to meet reliability, safety, and energy efficiency targets, performance incentive mechanisms are increasingly being used by regulators to address new challenges and opportunities facing the electric industry, ranging from smart grid adoption to clean energy goals. Synapse’s Utility Performance Incentive Mechanisms: A Handbook for Regulators, released this week on behalf of the Western Interstate Energy Board, provides detailed guidance for regulators on how to improve utility performance in a broad range of areas through well designed, strategically implemented incentive mechanisms.
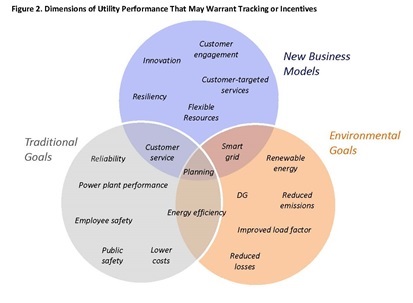
Performance metrics and incentives can serve as a valuable tool for monitoring and guiding utility actions. Specific metrics provide regulators with a window on how well a utility is operating, while financial rewards and penalties serve to better align the utility’s financial incentives with the public interest. Synapse’s handbook identifies many of the metrics and data sources available to measure utility performance, while discussing financial incentive design considerations.
By making regulatory goals and performance targets explicit, performance incentive mechanisms can address areas where historical utility performance has been unsatisfactory, or they can provide utilities with additional regulatory guidance for adopting innovative new technologies. The financial incentives inherent in performance incentive mechanisms could also serve as the foundation for new utility business models.
From Utility Performance Incentive Mechanisms: A Handbook for Regulators
However, performance incentive mechanisms also carry potential pitfalls. If not designed thoughtfully, they can provide rewards that are disproportionate to customer benefits, unintentionally shift attention from performance areas that do not have incentives, or prove to be a costly and time-consuming burden for all parties involved. Synapse’s handbook describes key design principles, discusses ways to avoid common pitfalls, and provides in-depth case studies that describe experience with performance incentive mechanisms from California to the United Kingdom.
Importantly, the authors prescribe an iterative process for developing performance incentive mechanisms. “The effectiveness of the mechanisms should be monitored closely and evaluated to determine which aspects are working well, and which are not,” they write. “Targets, financial incentives, and other components of the mechanisms may need to undergo several adjustments before they achieve their full potential.”
The handbook addresses implementation of incentive mechanisms in a variety of regulatory contexts. Whether regulators are operating in a state with cost-of-service regulation, with performance-based regulation, or are developing new regulatory and utility models, they will find relevant guidance for integrating performance incentive mechanisms into their regulatory structure in Utility Performance Incentive Mechanisms.